
Unique Anatomies
Patient-Matched
Solutions
MySpine Cervical is a patient-matched technology that assists in the placement of posterior cervical screws. The MySpine platform uses the patient’s spinal CT scan to create a 3D preoperative plan specific to that patient.
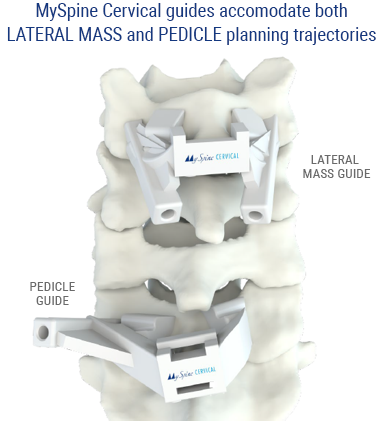
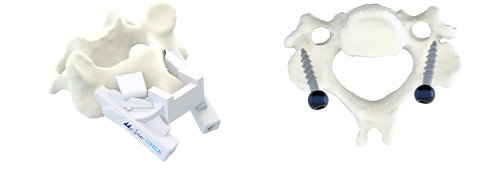
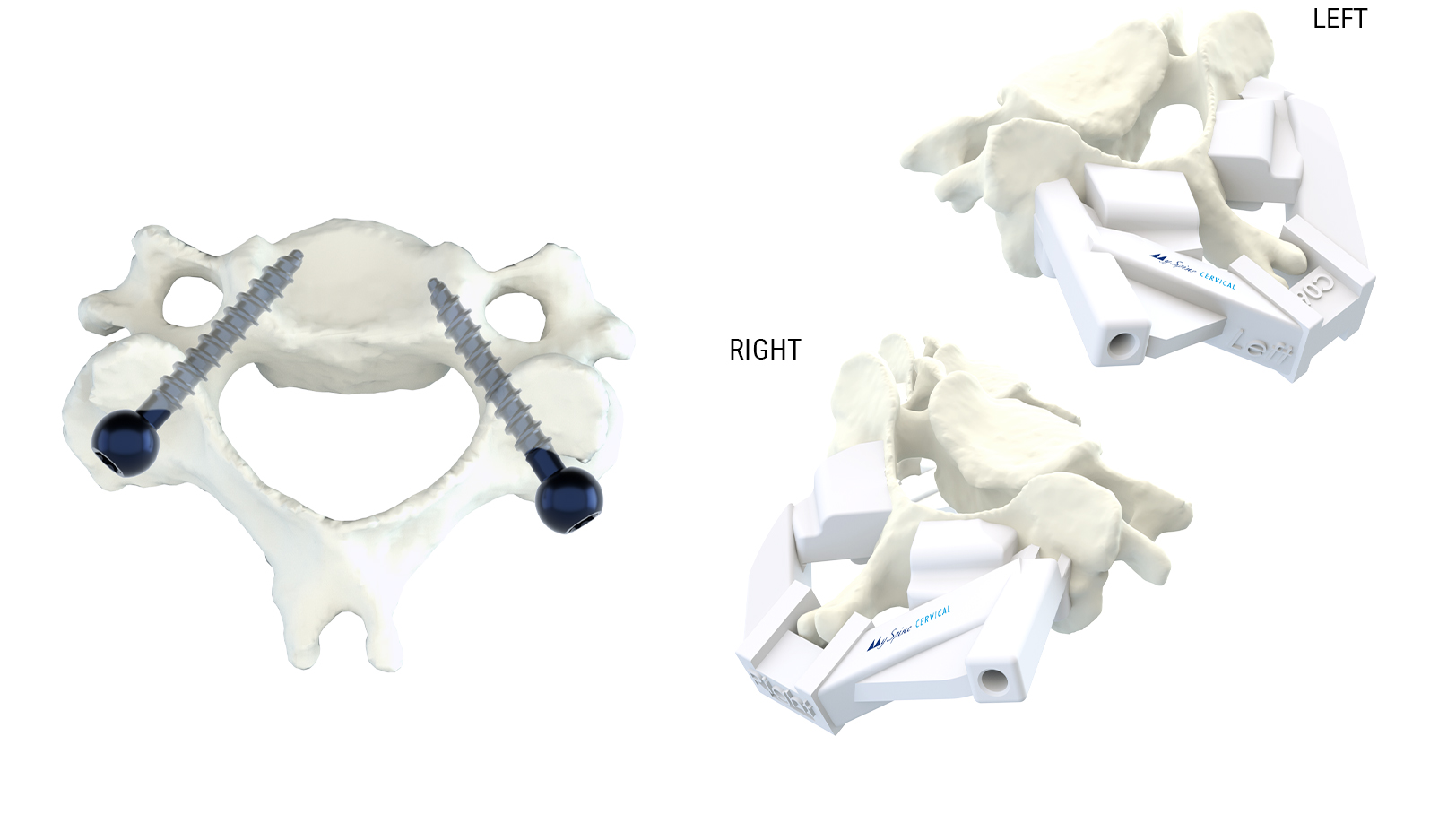
MySpine Cervical guides are patient-specific devices intended to be used as anatomical perforating guides, specific to a single patient’s anatomy, to assist intraoperatively in the positioning of screws during posterior cervical fixation surgery between the C2 to C7 levels.
[a] Cervical Spine: Anatomic Review. Global Spine Journal 2021.
[b] Ito Z. et al. Pedicle Screw Can be 4 Times Stronger Than Lateral Mass Screws for Insertion in the Midcervical Spine. Journal of Spinal Disorders and Techniques. 2014.

MySpine Cervical technology enhances surgical safety and accuracy by improving the precision of posterior cervical screw placement, leading to more reliable outcomes and greater confidence in the operating room[1,2].

Thanks to the one-to-one relationship between the vertebra and the guide, accuracy is not compromised by the mobility of the cervical spine, unlike with robot-assisted and navigation-guided systems, where such movements can affect precision. [3,4]

MySpine Cervical Technology is designed to assist in reducing surgical time and blood loss [2]. By providing precise guidance, it may help minimize the risk of complications.[1, 3, 4, 5]

By minimizing blood loss during surgery through MySpine Cervical, patients experience fewer complications, reduced need for blood transfusions, and a quicker recovery, all contributing to safer procedures[2].

Thanks to the low dose CT protocol and the diminishing radiation exposure during surgery, patients benefit from a lower risk of radiation-related complications, enhanced safety, and improved long-term health outcomes.[2,4]
[1] Oda I, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Accuracy of pedicle screw placement using patient-specific template guide system. J Orthopaedic Science. 2021 Jan.
[2] Farshad M. et al. Template guided cervical pedicle screw instrumentation. North American Spine Society Journal. 2022.
[3] Marengo N. et al. 3D-printed guides for cervical pedicle screw placement in primary spine tumor: Case report and technical description.
[4] Morello A. et al. Cervical Pedicle Screws: Multicenter Comparison of Freehand, Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Templates, Loop-X Navigation and O ARM/CT Navigation Accuracy and Safety. Global Spine Journal, 2025.
[5] Fukushima A. et al. Accuracy of cervical pedicle screw placement using a patient-specific template guide system and risk factor analysis for screw perforation: CT-based evaluation of 437 screws. European Spine Journal, 2025.
Accurate 3D preoperative planning based on a low dose CT scan delivers patient-matched guides, requiring zero capital investment.
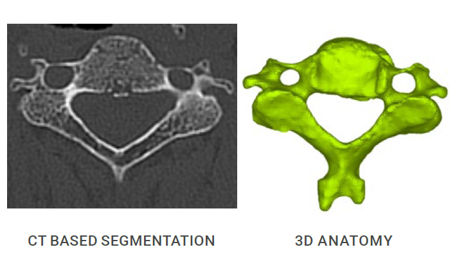
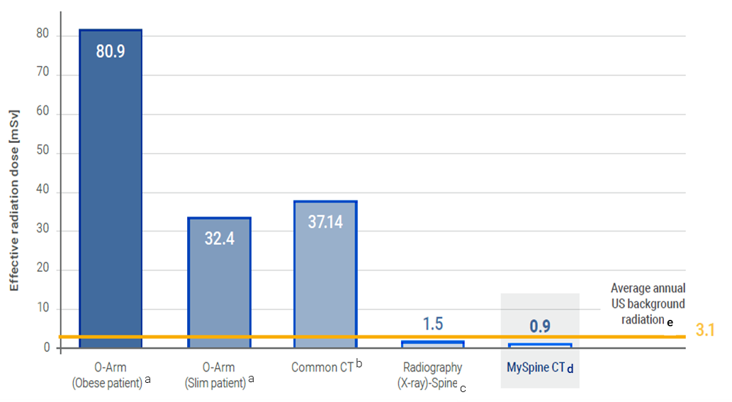
A specific low dose CT protocol ensures safe image acquisition, reducing the amount of irradiation absorbed by the patient. Preoperative planning potentially nullifies the need for intraoperative checks, with a dramatic reduction of irradiation.
The cumulative dose is potentially reduced compared to the navigation-assisted technique.
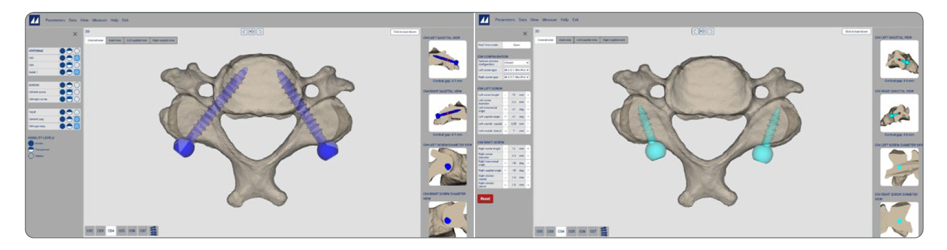
MySpine Cervical cases are managed entirely online with no need to install additional software. The case database is available to the surgeon anytime and anywhere. The information on the website is always kept up-to-date.

The MySpine guide is designed to match the vertebral anatomy of the patient and provide maximum stability on the vertebra, as well as correct placement of the screws. A plastic 3D model, which accurately replicates the patient’s vertebra, is provided to simulate the precise placement of the MySpine guide in the operating room.
Prior to the surgery, surgeons will receive the MySpine Cervical instruments and the plastic replica of the patient vertebrae. Medacta’s mission is to provide surgeons support through the M.O.R.E. Education Program. Upon request, the surgeon can receive the assistance of an experienced Medacta Proctoring Surgeon to assist with first surgeries in the local hospital or surgery center. With Medacta, the surgeon is never alone.
MySpine Cervical enhances accuracy and safety in the placement of M.U.S.T. MINI posterior cervical screws, while reducing surgical time and radiation exposure for both the patient and OR staff.[1,2]
The precision and safety of MySpine Cervical makes it a valuable navigation tool for pedicle screw insertion in the cervical spine.[2]
MySpine Cervical allows for precise screw insertion in the pedicle, while reducing the incidence of complications.[1,2]
The average operative time with MySpine Cervical was 168 minutes, compared to a range of 110-564 minutes with the free-hand technique. [2]
The median blood loss using MySpine Cervical was 300 mL, compared to a range of 150 - 1300 mL with the free-hand technique.[2]
[1] Oda, I, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Accuracy of pedicle screw placement using patient-specific template guide system. J. Orthopaedic Science, 2021 Jan.
[2] Farshad M. et al. Template guided cervical pedicle screw instrumentation. North American Spine Society Journal, 2022.
Patients are exposed to a low dose pre-op CT scan, resulting in radiation exposure lower than a single full spine x-ray.
Pre-operative planning potentially nullifies the need of intra-operative checks, with dramatic reduction of irradiation.[3,4]
The median intraoperative fluoroscopic dose was reduced to 321.2 mGycm2 vs. the standard range of 102.4 to 825.0 mGycm2. [2]
Cumulative dose is potentially reduced versus navigation assisted technique.
[2] Farshad M. et al. Template guided cervical pedicle screw instrumentation. North American Spine Society Journal, 2022.
[3] Farshad M. et al., Accuracy of patient-specific template-guided vs. free-hand fluoroscopically controlled pedicle screw placement in the thoracic and lumbar spine: a randomized cadaveric study, European Spine Journal, 2017.
[4] Chin K.R., Clinical Outcomes WIth Midline Cortical Bone Trajectory Pedicle Screws Versus Traditional Pedicle Screws in Moving Lumbar Fusions From Hospitals to Outpatient Surgery Centers
[2] Farshad M. et al. Template guided cervical pedicle screw instrumentation. North American Spine Society Journal. 2022.
[3] Marengo N. et al. 3D-printed guides for cervical pedicle screw placement in primary spine tumor: Case report and technical description.
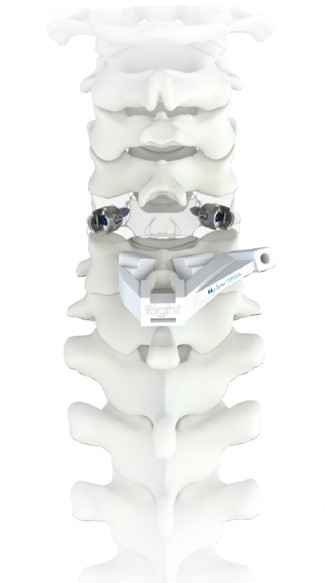
The M.U.S.T. MINI posterior cervical screw system is a comprehensive solution for fixation of the occipito-cervico-thoracic spine. The variety of screws, hooks, rods and connectors allows the surgeon to tailor the construct to the specific patient anatomy and pathology to be treated.
Increase SAFETY and ACCURACY of screw placement[1,2] with M.U.S.T. MINI
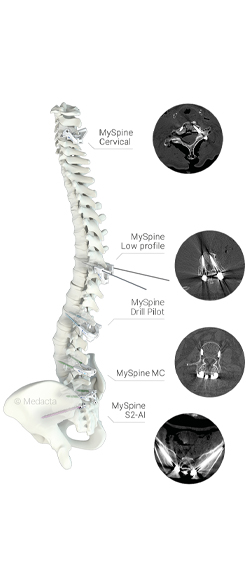
MySpine Cervical
MySpine Cervical guides are patient-specific devices intended to be used as anatomical perforating guides, specific to a single patient’s anatomy, to assist intraoperatively in the positioning of screws during posterior cervical fixation surgery between the C2 to C7 levels. MySpine Cervical guides accommodate both LATERAL MASS and PEDICLE planning trajectories.
MySpine
MySpine Pedicle Screw Placement guides are specifically developed for each individual patient:
- Standard MySpine guides are suitable for challenging deformities and long constructs.
- Low Profile MySpine guides are ideal for lower lumbar regions and degenerative cases.
MySpine MC
MySpine MC is a 3D printed patient-matched solution in the midline cortical approach. Posterior lumbar fusion is driven in a minimally invasive,[2] muscle sparing way,[3,4] allowing for shorter operating times. [3,5]
MySpine S2AI, MySpine Anchor
MySpine S2AI and MySpine Anchor are solutions for long constructs, designed to potentially overcome insufficient lower spine fixation.
[1] Oda I, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Accuracy of pedicle screw placement using patient-specific template guide system. J Orthopaedic Science. 2021 Jan.
[2] Farshad M. et al. Template guided cervical pedicle screw instrumentation. North American Spine Society Journal. 2022.
[3] Marengo N. et al. 3D-printed guides for cervical pedicle screw placement in primary spine tumor: Case report and technical description.
[4] Morello A. et al. Cervical Pedicle Screws: Multicenter Comparison of Freehand, Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Templates, Loop-X Navigation and O ARM/CT Navigation Accuracy and Safety. Global Spine Journal, 2025.
[5] Fukushima A. et al. Accuracy of cervical pedicle screw placement using a patient-specific template guide system and risk factor analysis for screw perforation: CT-based evaluation of 437 screws. European Spine Journal, 2025.
[6] Matsukawa K. et al., Comparison of safety and perioperative outcomes between patient-specific template-guided and fluoroscopic-assisted freehand lumbar screw placement using cortical bone trajectory technique, Global Spine Journal, 2022.
Miscellaneous